SAP goes cloud, who didn’t hear about that yet? It is the future product portfolio strategy from SAP, therefore SAP built an enterprise-ready data warehouse in the cloud namely SAP Data Warehouse Cloud. It provides an end-to-end data warehouse that has capabilities to combine data management processes with advanced analytics.
SAP Data Warehouse Cloud is meant to be a brand-new Data Warehousing solution, that can unite all your data sources in one central Data Store and maintain security, trust, and semantic richness of your information.
According to SAP portfolio, SAP Data Warehouse Cloud is:
- Collaborative
Designed for both enterprise IT and line of business users to manage and gain valuable insights
- End-To-End
Integrate data from any source and consume with powerful native analytics and business semantics
- Fast
Leverage the power of SAP HANA to instantly access the data you need, when you need it, without front-loaded costs
- Elastic
Only pay for what you use and reallocate resources quickly and easily across different use-cases and lines of business
SAP Data Warehouse Cloud isn’t just built for persons with strong IT affinity who create and model the data from scratch by themselves, but instead, it is built to collaborate between IT and business users, having a platform with self-service analytics in mind.
For this purpose, there is a so-called “space management concept” inside SAP Data Warehouse Cloud. A “Space” is a virtual workspace for an individual or a group of users for data modeling, data integration, and story dashboard building.

“Space” also makes it extremely easy to monitor which teams are using the most resources, with at a glance statistics including most used RAM and Storage. Resources can then be reallocated between teams, or storage and RAM limits can be changed depending on your organization’s current needs. Spaces are the starting point of SAP DWC where you can add users, connect to sources system, and manage other settings.
Depending on the authorization, only a user, who is assigned to a space, can build, or see a report, data model, and connections within the space. In this first part blog series, we will create a space together and on top of this space in the second part, we will create our data model. At the end of this blog series, we will build a dashboard, which is based on SAP BW Enterprise Procurement Model (EPM) like the picture below.
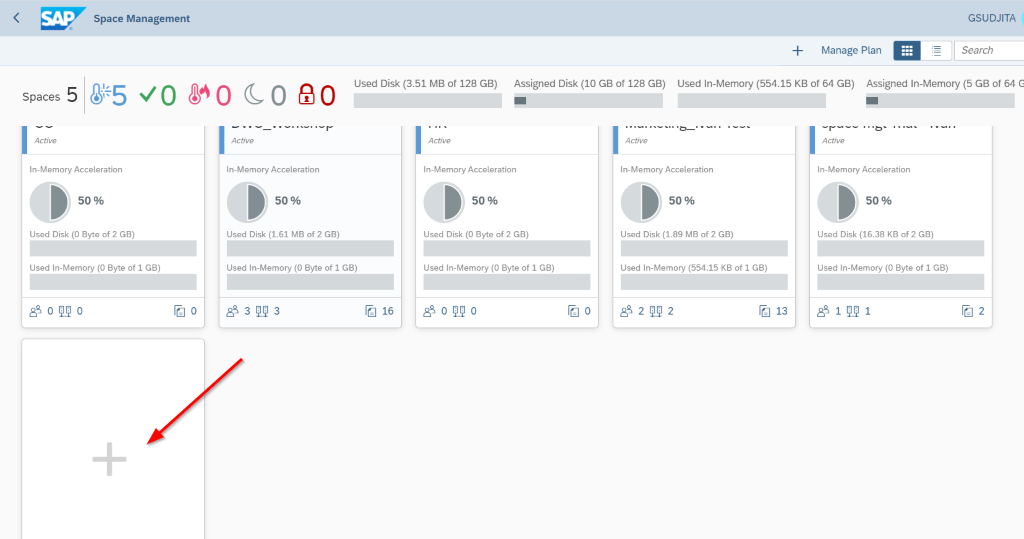
Doing so let us create our space, here in this screen you can click on the space management and create our new space.
As a second step, we click the + button and give it the desired name, in this case, I will give my space the name ZPBLOG

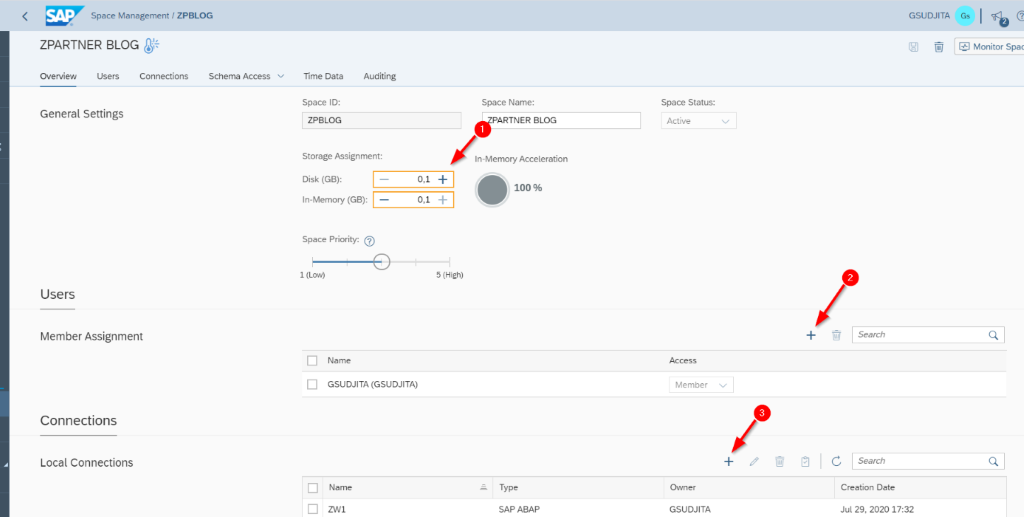
In the first step, we determine the size of disk management for this space, for our case, it would be enough to scale it to 0,1GB since our data volume is not so high and it is only for demo purposes.
After that, we must assign a user that will have access to this space so that the user can create a data model and dashboard on this space.
The next step is to establish connection between Data Warehouse Cloud and on-premises systems such as SAP ERP or SAP BW, to do this you have to install Data Provisioning Agent so that our SAP DWC can communicate with our SAP On-Premises System.
Last but not least don’t forget to save the new “space” so we can create a data model on it.
That’s it, in this blog part 1 you learned how to create a space, and in the next chapter, we will create our data model based on EPM model like we described above.
I hope you enjoy reading this blog and see you in the next chapter: http://test.zpartner.at/into-the-world-of-sap-datawarehouse-cloud-series-part-2/
